Invoice price method of consignment
Under invoice price method, the goods are consigned to the consignee at a price which is higher than their original cost. The proforma invoice is prepared by adding a certain percentage of the cost price or the sales price to the original cost of the goods. For example, A of Manchester consigns 1,000 boxes of goods to B of Glasgow on 1st June 2020. The cost per box is $50 and the proforma invoice is prepared to show a 20% profit on cost. In this example, the proforma invoice will be made at $60 (= $50 + 20% of $50) per box and the consignment account will be debited by $60,000, and not by $50,000.
The invoice price method is adopted to achieve one or more of the following purposes:
- Sending goods to consignee not at original cost but at a higher price helps keep the consignment profit secrete.
- It incentives consignee to realize the best possible price on sale of goods.
- It makes consignee charge uniform price to all the customers.
Journal entries under invoice price method
The preparation of journal entries and ledger accounts under invoice price method is much similar to cost price method, except for some adjusting entries required to remove excess price on goods and bring their value down to cost. This removal of excess price or loading is essential to know the actual profit earned from the consignment.
The journal entries that are made in the books of consignor under cost price method have been given here. In this article, we will discuss only those entries that are required to eliminate the impact of excess price or loading.
1. Journal entry for adjusting the value of opening stock
Stock reserve [Dr]
Consignment [Cr]
2. Journal entry for adjusting the value of goods sent on consignment:
Goods sent on consignment [Dr]
Consignment [Cr]
3. Journal entry for adjusting the value of abnormal loss:
Consignment [Dr]
Abnormal loss [Cr]
4. Journal entry for adjusting the value of stock on consignment:
Consignment [Dr]
Stock reserve [Cr]
When balance sheet is prepared at the end of accounting period, the balance of the stock reserve account is shown as deduction from the value of stock on consignment.
When consignment account is prepared at the start of next accounting period, the balance of the stock on consignment account appears on the debit side and the balance of stock reserve account appears on the credit side.
Example
Arif & Co. of Delhi consigned 100 units of goods, costing $100 per unit, to their agent Gupta & Co. in Mumbai at a proforma invoice of 20% on cost. Arif & Co. paid the following expenses:
- Loading charges: $100
- Freight: $200
- Insurance: $300
Gupta & Co. took delivery of goods and, on the same day, they sent a bank draft of $5,000 to Arif & Co. as advance against consignment.
Gupta & Co. forwarded an account sales revealing that 75 units were sold @ $140 per unit. Their expenses in respect of the consignment were as follows:
- Unloading charges: $75
- Carriage: $25
- Godown rent: $60
Gupta & Co. was allowed a commission of 10% on gross sale proceeds.
Required: Prepare journal eateries and draw up consignment account in the books of Arif & Co.
Solution
1. Journal entries in the books of Arif & Co:
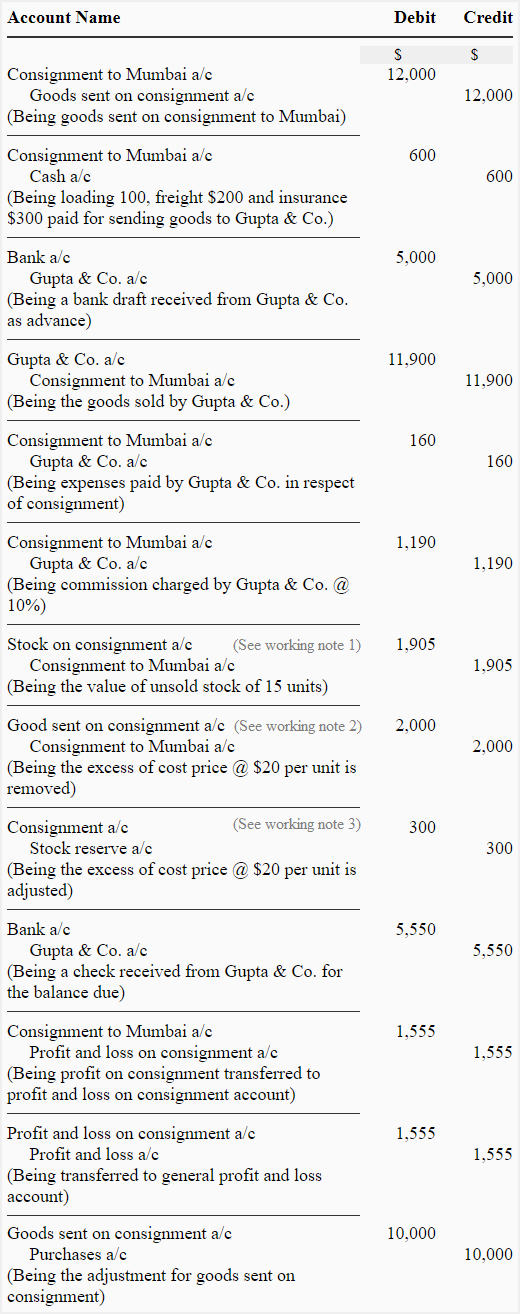
2. Consignment to Mumbai account
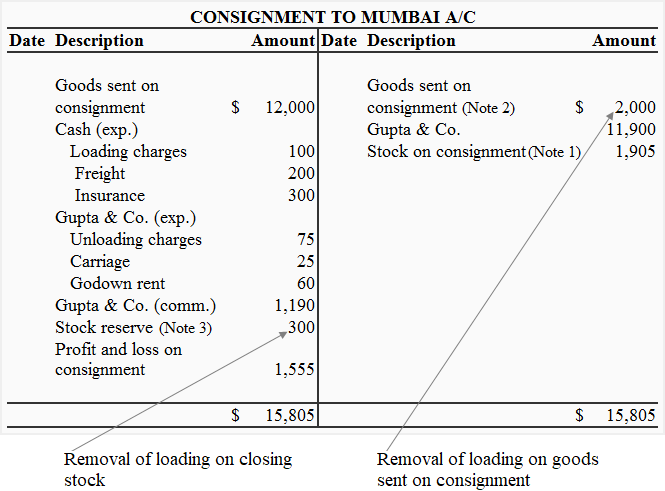
Notice that the loading on goods sent on consignment has been credited and the loading on closing stock has been been debited to the Consignment to Mumbai Account. This action removes the excess price that was added to the original cost of goods and is necessary to calculate the correct profit on consignment.
Working note 1: Calculation of stock on consignment:
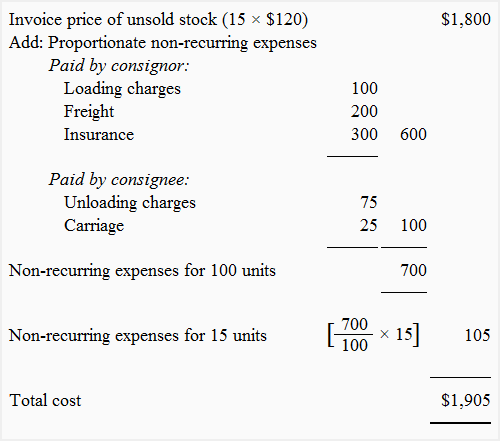
Working note 2: Calculation of excess price or loading on goods sent:
The goods were consigned at cost plus 20%. The cost of 100 units @ $100 is $10,000 and the excess price or loading can be computed as follows:
= ($12,000/120) × 20
= $2,000
or
100 units × $20
= $2,000
Working note 3: Calculation of excess price or loading on closing stock:
= (1,800/120) × 20
= $300
Or
15 units × $20
= $300

almost cleared thank you