Income statement
The income statement is an important financial statement that summarizes the operating results of the business by matching the revenue earned and expenses incurred to earn that revenue during a particular period of time. The revenue and expense figures used for the preparation of the income statement are directly taken from the adjusted trial balance. If revenue exceeds the total expenses, the income statement shows a net income for the period, but if, on the other hand, the total expenses exceed the revenue, it would show a net loss. The net income (or net loss) determined by the income statement is reported in the statement of retained earnings. It is, therefore, prepared first of all other financial statements.
Income statement is known by various names, such as statement of operations, earnings statement, and profit and loss statement.
Example:
Business Consulting Company prepares its adjusting entries at the end of each month. The adjusted trial balance of the company on December 31, 2015 is given below:
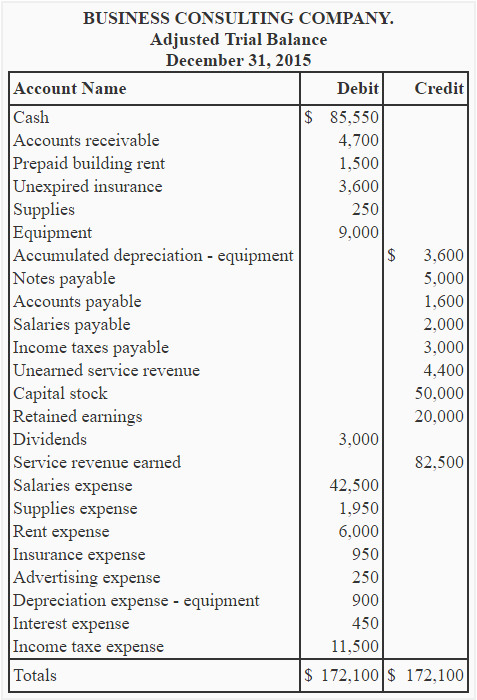
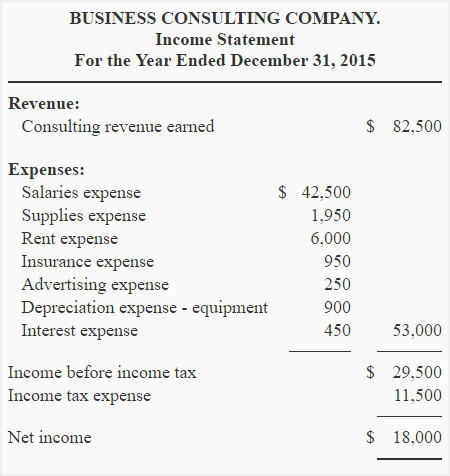
Required: Determine the net income (or net loss) of Business Consulting Company by preparing an income statement for the year ended December 31, 2015.
Solution:
Importance/Advantage of income statement:
The profit is the primary objective of every business. Various stakeholders, such as management, shareholders, investors, creditors, and even government agencies, have a keen interest in knowing the success of commercial entities in terms of their profitability. The companies periodically provide this information by preparing and publishing audited financial statements, including the income statement. Moreover, in many countries, publicly owned companies are legally required to prepare and publish an income statement as a part of their annual reports.
Limitations of income statement:
Income statement is of vital importance for the users of the financial statements. However, it suffers from the following limitations:
- The accounting process is based on various assumptions and estimates. Therefore, the net income (or net loss) measured by preparing an income statement is not absolutely accurate. An example of estimates used in the accounting process is the depreciation, which is computed on the basis of the estimated useful life of assets such as buildings, plants, equipment, etc.
- The use of judgments and estimates in the accounting process enables management to use such figures that would generate the desired net income (or net loss) figure for the period.
- A manipulation in net income is possible by using a particular inventory valuation method such as the FIFO, LIFO, or average costing method. The company’s management team may use such an inventory valuation method that generates the desired result for it.
- While preparing the income statement, we take into account only those activities whose value can be objectively measured. For example, a sound customer relations policy can develop a good customer base that can certainly be beneficial for profitable business operations, but its value cannot be objectively measured unless evidenced by an actual business transaction. The income statement doesn’t reflect the impact of such activities and efforts because they are not taken into account for accounting purposes.

How to prepare