Financing activities section of statement of cash flows
The financing activities section is the third and last section of the statement of cash flows that reports cash flows resulting from the financing activities of a business. It generally involves the flow of cash between the company and its sources of finance, i.e., owners and creditors. Here, the creditors mean the creditors for non-trading liabilities such as bonds payable and long-term loans, etc. The payments made to creditors for the purchase of raw materials or merchandise inventory are not included in the financing activities section. Such creditors are known as trade creditors, and cash paid to them is included in the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows.
Content:
- Examples of financing activities
- Understanding cash and non-cash financing activities
- Treatment of interest on debt and dividend on stock
- Format of financing activities section
- Example
Examples of financing activities
Some examples of cash flows from financing activities are listed below:
- Obtaining cash from common stockholders by issuing them the entity’s common stock.
- Obtaining cash from preferred stockholders by issuing them the preferred stock.
- Sale of treasury stock, if available.
- Issuance of long-term bonds payable.
- Payment of cash dividend to common stockholders.
- Payment of cash dividend to preferred stockholders.
- Purchase of treasury stock.
- Redemption of preferred stock.
- Redemption of bonds payable.
Understanding cash and non-cash financing activities
Financing activities may or may not involve the use of cash. Examples of financing activities that affect cash include issuing common or preferred stock for cash, issuing bonds for cash, obtaining a loan from a financial institution, etc. We report only those activities on the statement of cash flows that affect cash.
Those financing activities that have no impact on cash are known as “non-cash financing activities.” These activities are disclosed in the footnotes under the caption “non-cash investing and financing activities.” Examples of non-cash financing activities include converting a debt to common stock, converting preferred stock to common stock, and discharging a liability by issuing a note or a bond payable to the creditor.
Treatment of interest on debt and dividend on stock
Companies pay interest on debt and dividends on common and preferred stock. Both payments affect cash and therefore need to be disclosed in the statement of cash flows. Under US GAAPs, the interest paid by the entity must be treated as a cash outflow from operating activities, and the dividend paid on common or preferred stock must be treated as a cash outflow from financing activities. Under IFRS, companies can, however, treat both cash flows as either operating or financing cash flows. GAAPs, therefore, have more stringent guidelines in this regard.
Where a company chooses itself or is required by a jurisdictional law to prepare its financial statements in accordance with IFRSs, these cash flows must be disclosed on a consistent basis from period to period. For example, if an entity, reporting under IFRSs, lists both dividends and interest paid in the financing activities section, it should continue adopting this presentation in all subsequent years unless a change results in a better presentation or the change is suggested by IFRSs or some applicable law, etc.
Format of financing activities section
The format of financing activities section is usually much simpler and shorter than operating activities section. It is illustrated below:

Example
The following information has been extracted from the comparative balance sheet of James and Peter Company:
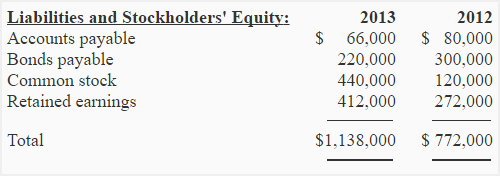
Additional information:
- James and Peter earned a net income of $250,000 for the year 2013 and paid a cash dividend of $110,000 during the year.
- The decrease in the amount of bonds payable represents their redemption during the year 2013.
- The increase in the amount of common stock represents the issuance of new common shares for cash during 2013.
Required: Calculate the net cash flows from financing activities of James and Peter Company during the year 2013.
Solution:

Working notes:
1. Redemption of bonds payable:
= $300,000 – $220,000
= $80,000
2. Sale of common stock:
= $440,000 – $120,000
= $320,000
3. Dividends paid:
$272,000 + $250,000 – $412,000
= $110,000
The decrease in accounts payable is used for calculating the cash paid to suppliers, which is an operating cash outflow.

Leave a comment