Exercise 4: Cost per equivalent unit – weighted average and FIFO method
Learning objective:
This exercise illustrates the preparation of a quantity schedule, the computation of equivalent units of production, and the determination of cost per equivalent unit under both FIFO and weighted average methods.
Alpha Global Inc. produces a product known as Antacid-ZX, an over-the-counter medicine used to neutralize stomach acidity. The processing of Antacid-ZX is completed in three separate departments. The data belonging to the first department for the month of March is given below:
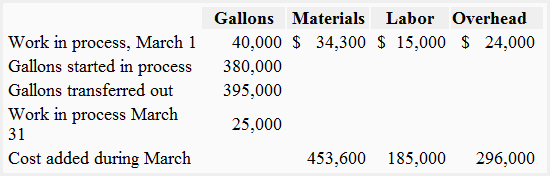
The stages of completion of beginning and ending work in process inventories with respect to materials and processing were as follows:
Beginning work in process inventory:
Materials: 80%
Processing: 75%
Ending work in process inventory:
Materials: 60%
Processing: 20%
Required: Make a quantity schedule, compute the equivalent units of production, and determine the cost per equivalent unit, assuming Alpha uses the following methods of accounting for units and costs:
- The Weighted average method
- The FIFO method
Solution
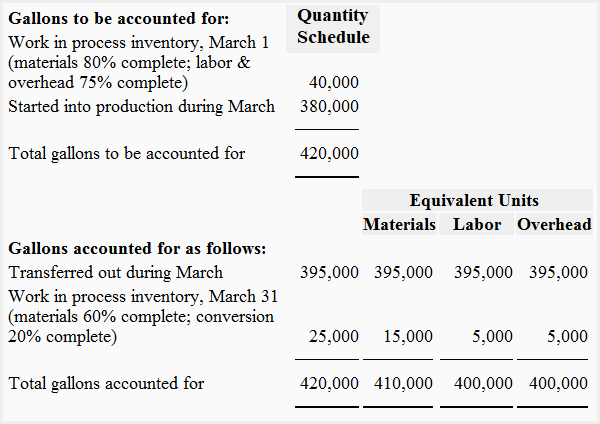
(1). Weighted average method
Quantity schedule and equivalent unit
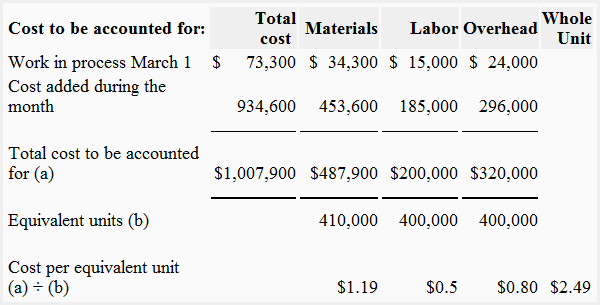
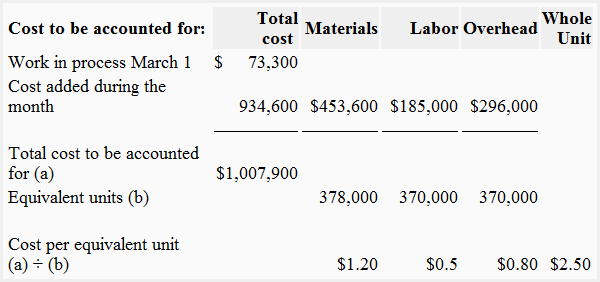
Cost per equivalent unit
2. FIFO method
Quantity schedule and equivalent units
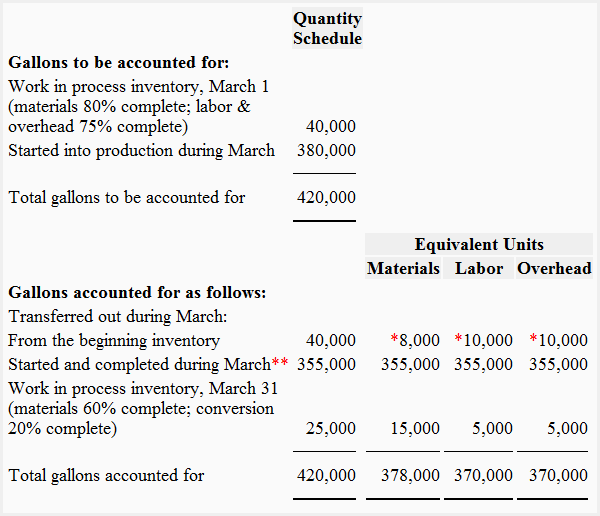
*Work required to complete gallons in work-in-process beginning inventory
Materials:
100% – 80% = 20%
40,000 × 20% = 8,000 gallons
Labor and overhead:
100% – 75% = 25%
40,000 × 25% = 10,000 gallons
**Started and completed during March:
= 380,000 gallons started – 25,000 gallons in work-in-process ending inventory
= 355,000 gallons started and completed during March
or
= 395,000 gallons started – 40,000 gallons in beginning work-in-process inventory
= 355,000 gallons started and completed during March
Cost per equivalent unit

Leave a comment