Capital and revenue receipts
Business receipts are inflow of economic resources mostly in the form of cash and cash equivalents. In accounting and finance, they can be divided into two types – capital receipts and revenue receipts. A brief explanation of both the types is given below:
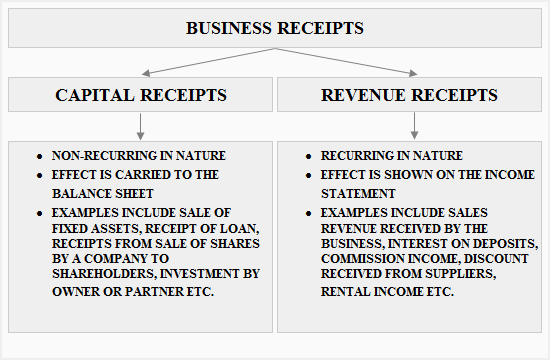
Capital receipts
Capital receipts are business receipts which are not related to the day to day business activities of a company. They occur occasionally and provide benefit for a long period of time.
Capital receipts are normally presented in the balance sheet of a company when realized and generally occur as a result of the following events:
- Sale of fixed assets
- Issuance of capital in the form of shares
- Issuance of debt instruments
Suppose, in annual general meeting of a QRS company, the issue of right shares was approved at the rate of $8 per share. QRS allocated shares to all the existing members of the company proportionately and in return received cash. The cash received by QRS company was a capital receipt. The company debited its bank account and credited its equity account in the books of accounts.
Other common examples of capital receipts
- Cash received from sale of fixed assets.
- Amount of loan received by the company from a bank.
- Capital invested in the business by a new partner.
- Consideration received by a company through sale of its license to produce a well marketed drug to another company
Revenue receipts
Revenue receipts are receipts that occur routinely. They are realized from day to day business activities of a company and are needed by any business to survive and strive. Revenue receipts are normally received through the sale of stock-in-trade and the provision of services to customers in the ordinary course of business. The effect of revenue receipts is normally shown only in the income statement of the company.
Suppose CDE Company is in the business of manufacturing and selling baby diapers them in bulk to wholesalers and retailers. CDE invoices its customers on receipt of goods by them and maintains an average collection period of 30 days. CDE records its sale/revenue on receipt of goods by the customers. The sales revenue received by CDE company is a revenue receipt.
Common examples of revenue receipts
- Revenue received from sale of goods to customers.
- Revenue received from provision of services to clients
- Income received as interest on a saving account.
- Dividend income received from shares of various companies.
- Rental income received by a company.
- Bad debts recovered by a company
- Cash discount received from vendors.
- Commission income received by a company.
Summary and conclusion
- Capital receipts are inflow of economic resources to the company and are non-recurring in nature. Their effect is carried only to the balance sheet of company
- Revenue receipts are inflow of economic resources to the company and are recurring in nature. They are vital to keep the company running. Their effect is only shown in the income statement of a company.
- Capital receipts and revenue receipts should never be confused with each other as it can lead to classification errors and an incorrect financial summary report.

Leave a comment